South Korea faces a new cyber threat as hackers utilize an open-source rootkit known as Reptile to breach Linux systems.
A report published this week by AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC) reveals that Reptile is a complex rootkit malware that offers a reverse shell, enabling attackers to gain unauthorized control of infected systems. Unlike conventional rootkit malware, which usually hides its activities, Reptile takes a more invasive approach.
ASEC explains a technique known as “port knocking,” where the malware opens a specified port on the affected system and awaits a particular packet, known as a “magic packet,” from the threat actor. This enables a connection with the command-and-control (C&C) server.
Reptile, a malicious software designed to gain privileged root-level access to a machine, has been deployed in at least four different instances since 2022.
It was first associated with an Earth Berberoka intrusion (also called GamblingPuppet) by Trend Micro in May 2022. This specific attack targeted gambling sites in China, using the malware to mask connections and processes related to a Python trojan named Pupy RAT.
In March 2023, Google’s Mandiant uncovered a series of attacks by a possible China-linked entity known as UNC3886, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities in Fortinet devices to distribute Reptile along with custom implants.
Furthermore, ExaTrack exposed a Chinese hacking team’s utilization of Linux malware called Mélofée, based on Reptile, in the same month. Microsoft found a cryptojacking operation in June 2023 that used Reptile to hide its activities.
A more in-depth investigation into Reptile shows a loader that employs a tool called kmatryoshka, which decrypts and loads the rootkit’s kernel module into memory, subsequently opening a specific port and waiting for a magic packet.
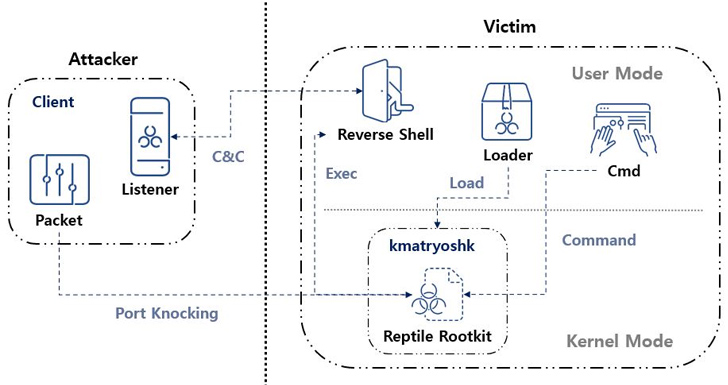
ASEC highlighted the mechanism of using magic packets to trigger the malicious behavior, which has similarities with another rootkit, Syslogk, detailed by Avast in the past.
Reptile’s effects in South Korea include cases involving Mélofée-like tactics. ASEC describes Reptile as “a Linux kernel mode rootkit malware that provides a concealment feature for files, directories, processes, and network communications.” This rootkit’s reverse shell feature also makes affected systems prone to takeover by attackers.
This news comes on the heels of recent discoveries of multiple new variants of an elusive Linux backdoor known as BPFDoor, attributed to a Chinese threat actor codenamed Red Menshen (also referred to as DecisiveArchitect or Red Dev 18). Trend Micro notes a six-fold enhancement in BPFDoor’s instructions, indicating its continued success and development.
The presence of Reptile and the rapid evolution of other threats like BPFDoor signal a growing need for robust security measures against increasingly sophisticated Linux-targeting malware.
Found this news interesting? Follow us on Twitter and Telegram to read more exclusive content we post.


